Living With Natural Gas Pipelines: Appalachian Landowners Describe Fear, Anxiety and Loss

In this Feb. 13, 2015, file photo, a worker shields his face against temperatures in the teens as he guides a section of pipe while working on a shale gas pipe line in Zelienople, Pa. AP Photo/Keith Srakocic, File
COMMENTARY | Many of the lines were built in the past five years. While energy companies promise economic benefits for depressed regions, the projects often upend the lives of people in their paths.
More than 2 million miles of natural gas pipelines run throughout the United States. In Appalachia, they spread like spaghetti across the region.
Many of these lines were built in just the past five years to carry natural gas from the Marcellus Shale region of Ohio, Pennsylvania and West Virginia, where hydraulic fracturing has boomed. West Virginia alone has seen a fourfold increase in natural gas production in the past decade.
Such fast growth has also brought hundreds of safety and environmental violations, particularly under the Trump administration’s reduced oversight and streamlined approvals for pipeline projects. While energy companies promise economic benefits for depressed regions, pipeline projects are upending the lives of people in their paths.
As a technical and professional communication scholar focused on how rural communities deal with complex problems and a geography scholar specializing in human-environment interactions, we teamed up to study the effects of pipeline development in rural Appalachia. In 2020, we surveyed and talked with dozens of people living close to pipelines in West Virginia, Ohio and Pennsylvania.
What we found illuminates the stress and uncertainty that communities experience when natural gas pipelines change their landscape. Residents live with the fear of disasters, the noise of construction and the anxiety of having no control over their own land.
‘None of This is Fair’
Appalachians are no strangers to environmental risk. The region has a long and complicated history with extractive industries, including coal and hydraulic fracturing. However, it’s rare to hear firsthand accounts of the long-term effects of industrial infrastructure development in rural communities, especially when it comes to pipelines, since they are the result of more recent energy-sector growth.
For all of the people we talked to, the process of pipeline development was drawn out and often confusing.
Some reported never hearing about a planned pipeline until a “land man” – a gas company representative – knocked on their door offering to buy a slice of their property; others said that they found out through newspaper articles or posts on social media. Every person we spoke with agreed that the burden ultimately fell on them to find out what was happening in their communities.
One woman in West Virginia said that after finding out about plans for a pipeline feeding a petrochemical complex several miles from her home, she started doing her own research. “I thought to myself, how did this happen? We didn’t know anything about it,” she said. “It’s not fair. None of this is fair. … We are stuck with a polluting company.”
‘Lawyers Ate Us Up’
If residents do not want pipelines on their land, they can pursue legal action against the energy company rather than taking a settlement. However, this can result in the use of eminent domain.
Eminent domain is a right given by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission to companies to access privately held property if the project is considered important for public need. Compensation is decided by the courts, based on assessed land value, not taking into consideration the intangibles tied to the loss of the land surrounding one’s home, such as loss of future income.
Through this process, residents can be forced to accept a sum that doesn’t take into consideration all effects of pipeline construction on their land, such as the damage heavy equipment will do to surrounding land and access roads.
One man we spoke with has lived on his family’s land for decades. In 2018, a company representative approached him for permission to install a new pipeline parallel to one that had been in place since 1962, far away from his house. However, crews ran into problems with the steep terrain and wanted to install it much closer to his home. Unhappy with the new placement, and seeing erosion from pipeline construction on the ridge behind his house causing washouts, he hired a lawyer. After several months of back and forth with the company, he said, “They gave me a choice: Either sign the contract or do the eminent domain. And my lawyer advised me that I didn’t want to do eminent domain.”
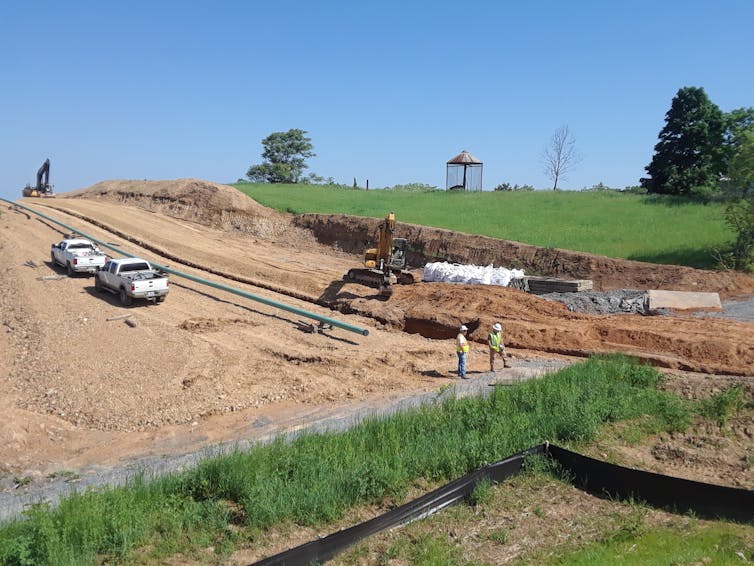

There was a unanimous sense among the 31 people we interviewed that companies have seemingly endless financial and legal resources, making court battles virtually unwinnable. Nondisclosure agreements can effectively silence landowners. Furthermore, lawyers licensed to work in West Virginia who aren’t already working for gas companies can be difficult to find, and legal fees can become too much for residents to pay.
One woman, the primary caretaker of land her family has farmed for 80 years, found herself facing significant legal fees after a dispute with a gas company. “We were the first and last ones to fight them, and then people saw what was going to happen to them, and they just didn’t have – it cost us money to get lawyers. Lawyers ate us up,” she said.
The pipeline now runs through what were once hayfields. “We haven’t had any income off that hay since they took it out in 2016,” she said. “It’s nothing but a weed patch.”
‘I Mean, Who Do You Call?’
Twenty-six of the 45 survey respondents reported that they felt that their property value had decreased as a result of pipeline construction, citing the risks of water contamination, explosion and unusable land.
Many of the 31 people we interviewed were worried about the same sort of long-term concerns, as well as gas leaks and air pollution. Hydraulic fracturing and other natural gas processes can affect drinking water resources, especially if there are spills or improper storage procedures. Additionally, methane, a potent greenhouse gas, and volatile organic compounds, which can pose health risks, are byproducts of the natural gas supply chain.
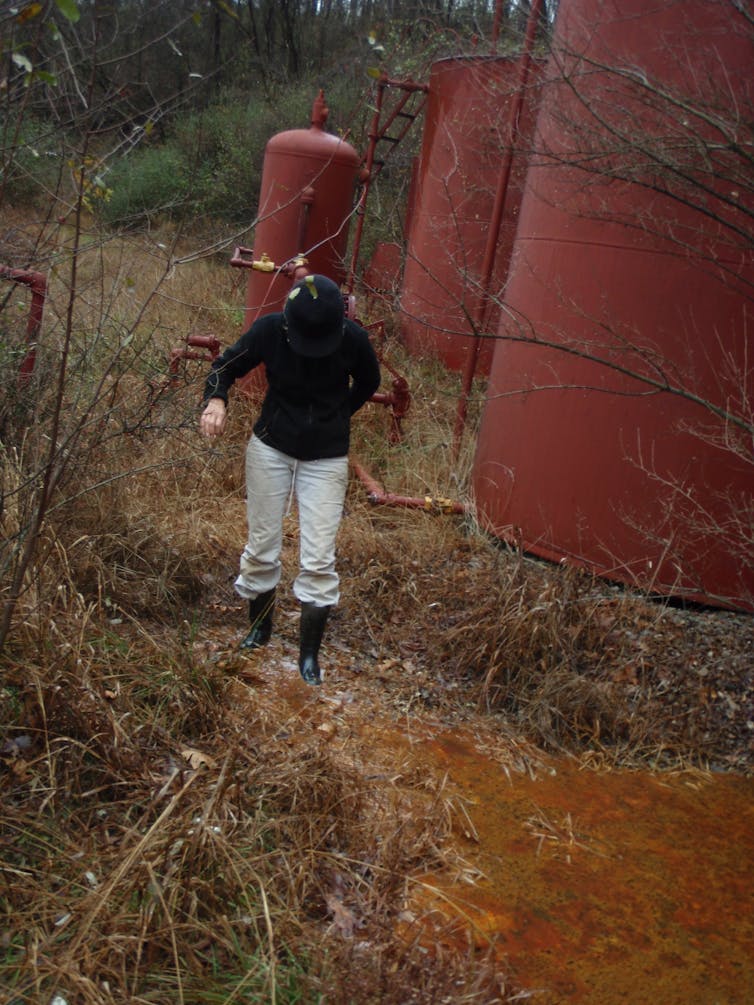

“Forty years removed from this, are they going to be able to keep track and keep up with infrastructure? I mean, I can smell gas as I sit here now,” one man told us. His family had watched the natural gas industry move into their part of West Virginia in the mid-2010s. In addition to a 36-inch pipe on his property, there are several smaller wells and lines. “This year the company servicing the smaller lines has had nine leaks … that’s what really concerns me,” he said.
The top concern mentioned by survey respondents was explosions.
According to data from 2010 to 2018, a pipeline explosion occurred, on average, every 11 days in the U.S. While major pipeline explosions are relatively rare, when they do occur, they can be devastating. In 2012, a 20-inch transmission line exploded in Sissonville, West Virginia, damaging five homes and leaving four lanes of Interstate 77 looking “like a tar pit.”
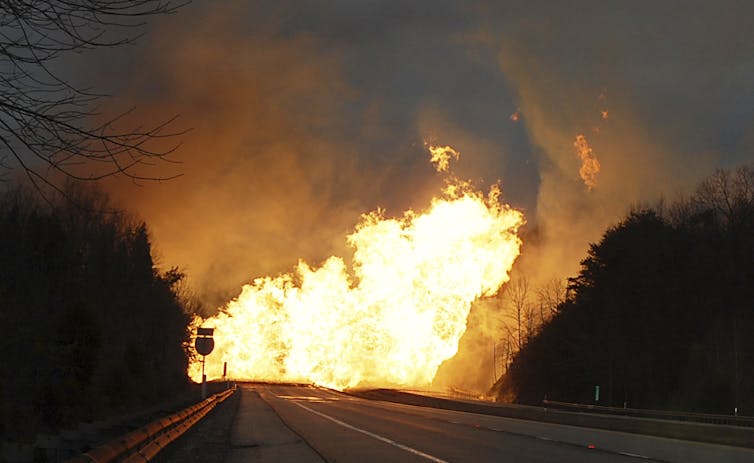

Amplifying these fears is the lack of consistent communication from corporations to residents living along pipelines. Approximately half the people we interviewed reported that they did not have a company contact to call directly in case of a pipeline emergency, such as a spill, leak or explosion. “I mean, who do you call?” one woman asked.
‘We Just Keep Doing the Same Thing’
Several people interviewed described a fatalistic attitude toward energy development in their communities.
Energy analysts expect gas production to increase this year after a slowdown in 2020. Pipeline companies expect to keep building. And while the Biden administration is likely to restore some regulations, the president has said he would not ban fracking.
“It’s just kind of sad because they think, once again, this will be West Virginia’s salvation,” one landowner said. “Harvesting the timber was, then digging the coal was our salvation. … And then here’s the third one. We just keep doing the same thing.”
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
[Deep knowledge, daily. Sign up for The Conversation’s newsletter.]
![]()
Erin Brock Carlson is an assistant professor of professional writing and editing at West Virginia University. Martina Angela Caretta is a senior lecturer in human geography at Lund University.
NEXT STORY: MilCloud adds AWS option





